
Let’s go , it’s time to analyze and understand the iconic Hadoop Ecosystem. The first thing that you should know Hadoop is an open-source technology of Google Inc´s, Google File System (GFS) & the name Hadoop is not an acronym. The project´s creator Doug Cutting, explains how the name came about:

“The name my kid gave a stuffed yellow elephant. Short, relatively easy to spell and pronounce, meaningless, and not used elsewhere: those are naming criteria. Kids are good at generating such. Googol is a kid´s term.”
Hadoop is a distributed data store that provides a platform for implementing powerful parallel processing frameworks. The reliability of this data store when it comes to storing massive volumes of data, coupled with its flexibility in running multiple processing frameworks makes it an ideal choice for your data hub. This characteristic means that you can store any type of data: (structured, semi-structured, quasi-structured & unstructured).
The Schema-on-Read refers to the fact that raw, unprocessed data can be loaded in Hadoop, with the structure imposed at processing time based on the requirements of the processing application. And the other hand , Schema-on-Write is generally used with traditional data management systems. Such systems require the schema of the data store to be defined before the data can be loaded.
There are many factors that you should take into consideration before dumping your data into Hadoop:
- Data storage formats. There are a number of file formats and compression formats supported Hadoop.
- Multitenancy. It’s common for clusters to host multiple users, groups and application types.
- Schema design. This includes directory structures for data loaded into HDFS
- Metadata management. As with any data management system, metadata related to the stored data is often as the data itself.
Hadoop Ecosystem general view
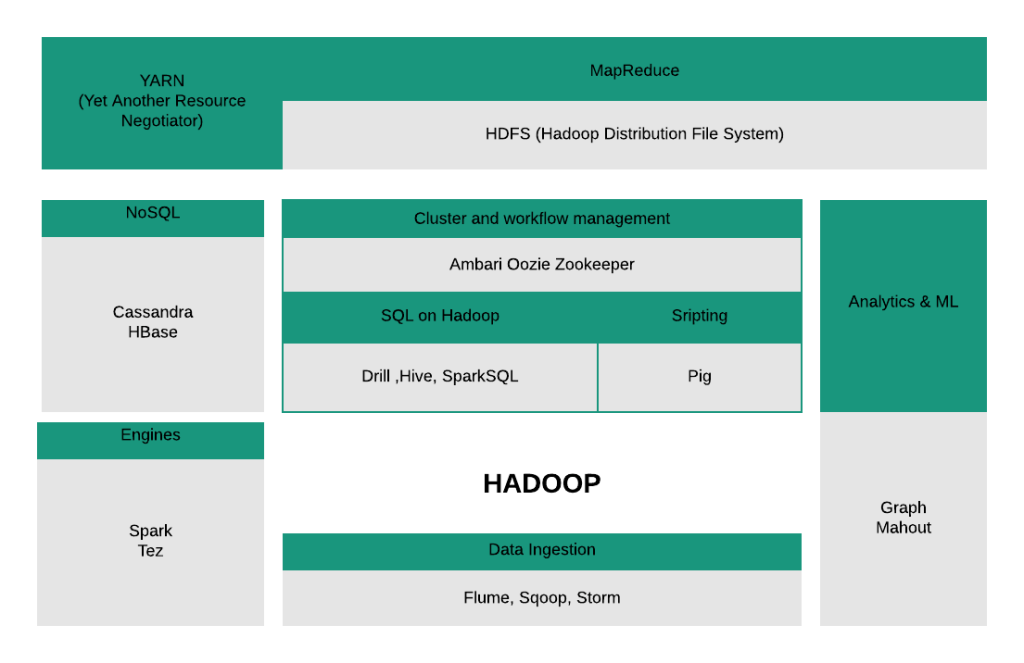
Four main components of Apache Hadoop
Apache Hadoop Common
Hadoop module is a Hadoop Base API (jar file) for all Hadoop components. All other components work on top of this module. Hadoop provides two operational modes, where each mode supports a type of interaction with MapReduce & HDFS. Java MapReduce mode writes the mapper, combiner, and reducer functions in Java. For the other hand, streaming mode supports standard nix streams and nix pipe mechanisms. This means that all the MapReduce functions can be written in any programming or scripting languages (C, Ruby, Python, Perl, etc).
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System)
Distributed file system designed to run on commodity hardware for storing large files of data with streaming data access patterns. HDFS is highly fault-tolerant and is designed to be deployed on low-cost hardware. Provides high throughput access to application data and is suitable for applications that have large data sets. HDFS relaxes a few POSIX requirements to enable streaming access to file system data.
HDFS has a master/slave architecture. An HDFS cluster consists of a single NameNode, a master server that manages the file system namespace and regulates access to files by clients. The DataNodes, usually one per node in the cluster, manage storage attached to the nodes that they run on & are used as common storage for blocks (128 MB) by NameNodes. Are responsible for serving read and write requests from the file system’s clients.
The DataNodes also perform block creation, deletion, and replication upon instruction from the NameNode.
MapReduce
Grace Hooper´s quote that the fundamental paradigm of MapReduce:
“Is the reduction in time to complete a given task by breaking it down into stages and then executing those stages in parallel”
A MapReduce job usually splits the input data-set into independent chunks which are processed by the map tasks in a completely parallel manner.The framework sorts the output of the maps, which are then input to the reduce tasks. Typically both the input and the output of the job are stored in a file-system.The framework takes care of scheduling tasks, monitoring them and re-executes the failed tasks. MapReduce is programming in Java.
The MapReduce framework operates exclusively on <key, value> pairs, that is, the framework views the input to the job as a set of <key, value> pairs and produces a set of <key, value> pairs as the output of the job.
(input) <k1, v1> ->
map -> <k2, v2> ->
combine -> <k2, v2> ->
reduce -> <k3, v3> (output)
Common uses:
- Word count
- Reverse index
- tf-idf
- Distributed grep and distributed object recognition
- Distributed associative aggregation
YARN (Yet Another Resource Negotiator)
Is a Hadoop ecosystem component that provides the resource management & is the most important component. Is called the operating system of Hadoop, as it is responsible for managing and monitoring workloads.It allos multiple data processing engines, such real-time streaming and batch processing.
The fundamental idea of YARN is to split up the functionalities of resource management and job scheduling/monitoring into separate daemons. The idea is to have a global ResourceManager (RM) and per-application ApplicationMaster (AM). An application is either a single job or a DAG of jobs.
Features of YARN are: flexibility, efficiency, shared and scalability.
Other Hadoop projects:
| Ambari | Ambari also provides a dashboard for viewing cluster health such as heatmaps and ability to view MapReduce, Pig and Hive applications visually alongwith features to diagnose their performance characteristics in a user-friendly manner. |
| Cassandra | A scalable multi-master database with no single points of failure. |
| HBase | A scalable, distributed database that supports structured data storage for large tables. |
| Hive | A data warehouse infrastructure that provides data summarization and ad hoc querying. |
| Mahout | Scalable machine learning and data mining library. |
| Pig | A high-level data-flow language and execution framework for parallel computation. |
| Spark | Provides a simple and expressive programming model that supports a wide range of applications, including ETL, machine learning, stream processing, and graph computation. |
| ZooKeeper | A high-performance coordination service for distributed applications. |
Hadoop is an ecosystem that provides a framework to deal with Big Data and help us handle the three V´s (Velocity, Volume & Variety). Also, enables us to use parallel processing capability to handle huge volumes of data using flexible commercial grade infrastructure. This post has the principal tools and frameworks to generate a general point of view of Hadoop Ecosystem. We need remember that these technologies have many updates around the year & a good practice is to consult the documentation. In Big Data projects it’s very important to understand the business problem to generate great analytical solutions. The other technologies that propose other solutions are: Cloudera, ElasticSearch, Dremio, Confluent, etc. In the next post we will analyze these technologies and compare their functionalities, advantages and challenges.
Written by Irving Ariel
White T. (April 2015). Hadoop: The Definitive Guide, Fourth Edition. United States of America: O´Reilly.
Borthakur D. (2021). HDFS Archiecture guide. April 22, 2021, de Apache Softwre Foundation Sitio web: https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r1.2.1/hdfs_design.html
The Apache Software Foundation.. (October 10, 2020). Hadoop Deployment Layout. April 22, 2021, de The Apache Software Foundation. Sitio web: https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r1.2.1/deployment_layout.html
The Apache Software Foundation. (September 06, 2020). Apache Hadoop YARN. April 22, 2021, de The Apache Software Foundation Sitio web: https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html